Where the techniques of Maths
are explained in simple terms.
Algebra - Absolute value equations.
Comments about graphing.
- Algebra & Number
- Calculus
- Financial Maths
- Functions & Quadratics
- Geometry
- Measurement
- Networks & Graphs
- Probability & Statistics
- Trigonometry
- Maths & beyond
- Index
A basic equation of the form y = 2x + 1 is graphed as a straight line with
- a gradient of 2;
- an x intercept at x = -½
- a y intercept at y = 1.
The graph of the line extends in two directions - up from the x-axis and down below the x-axis.
An absolute value equation of the form y = |2x + 1| is developed from that original by taking the section below the x axis and reflecting it around the x axis. Such an equation cannot be graphed below the horizontal axis - except if there is a negative sign outside the absolute value signs. For example y = -|2x + 1| would only be below the axis and not above.
So an easy way to graph an absolute value line is to draw the graph of the original equation and then reflect any part which is below the x axis.
| Basic equation | y = 2x + 1 | y = x2 - 2 | y = -(2 - 3x) |
| Graph | 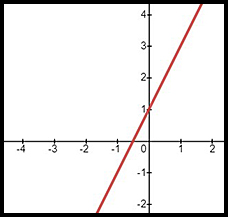 |
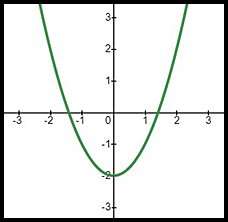 |
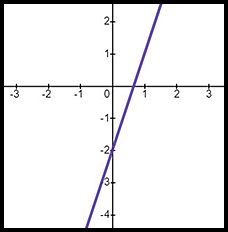 |
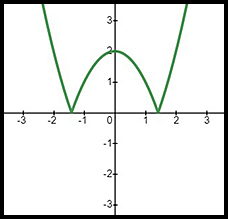
| Absolute value equation | y = |2x + 1| | y = |x2 - 2| | y = -|2 - 3x| |
| Graph | 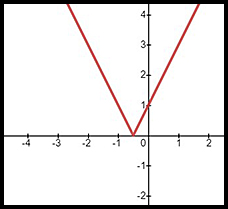 |
 |
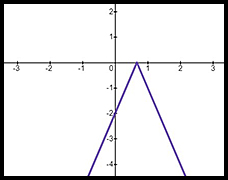 |
| Note reflection for x < -0.5 |
Note reflection about the x axis between x = -√2 and x = + √2 | Note reflection to under the x axis holding x = 0.67 as the reflection point. |